Heat Seal-Know How 1
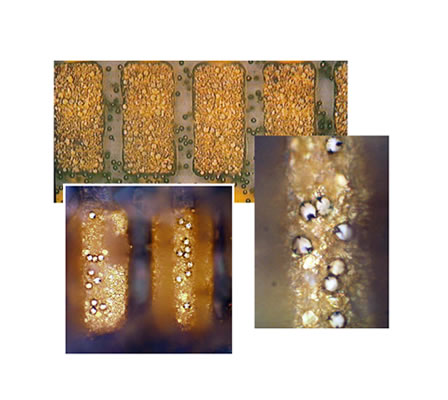
Heat seal joints are carried out with so-called âanisotropically conductive adhesivesâ. In this way, for example, flexible foils are contacted with conductor paths (FPC) on circuit boards or the glass-connection face of an LCD or OLED module.
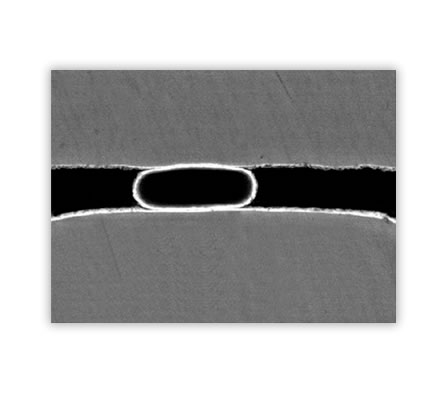
Anistropic adhesives are filled with electrically conductive particles. These particles are so small that an electrically conductive connection in the X- or pressure direction is created, while there is no contact in the Z-direction. On the application of heat (around 140ºC) and pressure (14-17 Kg/cm²), the adhesive begins to flow. When the adhesive cools under pressure, the conductive particles are âfrozenâ in position and retain their conductivity. The adhesive has a good mechanical strength after cooling.
Typical abbreviations for such adhesives are:
ACA â anisotropic conductive adhesive
ACF â anisotropic conductive film
ACP â anisotropic conductive paste. (liquid adhesive)